04 Dec What Your CBC Panel is Telling You
When you receive your blood test results, you’re presented with a series of numbers and acronyms—RBC, WBC, and Hgb, among others. These are not just random figures but important indicators of your health status. Let’s unpack the Complete Blood Count (CBC) and explore what these numbers mean.
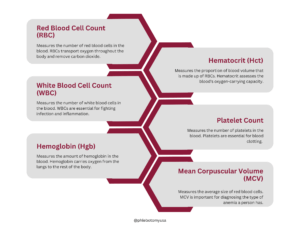
Red Blood Cell Count (RBC)
Red blood cells carry oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body and bring back carbon dioxide to be expelled. The RBC count indicates how many red blood cells are in your blood. Low counts could signal anemia, causing fatigue and weakness, while high counts may suggest dehydration or heart conditions.
Normal Range:
-
- Men: 4.5-5.9 million cells/mcL
- Women: 4.1-5.1 million cells/mcL
White Blood Cell Count (WBC)
White blood cells are the defenders of your immune system, fighting infections and inflammation. A high WBC count could indicate an infection or an inflammatory disease, and a low count might show a compromised immune system, possibly due to a medical condition or certain medications.
Normal Range:
-
- 4,500 to 11,000 cells/mcL
Hemoglobin (Hgb)
Hemoglobin is the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. Abnormally low hemoglobin levels can be a sign of anemia, while unusually high levels might indicate a condition leading to an excess production of red blood cells.
Normal Range:
-
- Men: 13.8-17.2 grams/dL
- Women: 12.1-15.1 grams/dL
Hematocrit (Hct)
Hematocrit measures the volume of red blood cells compared to the total blood volume. Low hematocrit levels suggest anemia, and high levels could be a sign of dehydration or polycythemia vera, a condition where the body produces too many red blood cells.
Normal Range:
-
- Men: 40.7-50.3%
- Women: 36.1-44.3%
Platelet Count
Platelets are cell fragments that play a crucial role in blood clotting. A low platelet count can lead to easy bruising or bleeding, known as a bleeding disorder. A high count can increase the risk of thrombosis, where blood clots form in blood vessels.
Normal Range
-
- 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/mcL
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
MCV indicates the average size of your red blood cells and helps classify anemia types. Small-sized red blood cells (microcytic anemia) often point to iron deficiency, while large-sized cells (macrocytic anemia) may suggest a deficiency in vitamin B12 or folate.
Normal Range
-
- 80-100 fL
Conclusion
A CBC is more than a routine test; it’s a window into your health that can lead to early disease detection and management. By understanding your CBC, you’re better equipped to engage in informed discussions about your health with your healthcare provider.